When you hear the term “business,” what do you think of? Do you think of businesses in general? Do you think of the study of business, like we’re doing now? Do you think of a small mom-and-pop grocery store down the street or, perhaps, a larger company? This tutorial will cover the meaning of the term “business” and provide an overview of the basics of business. Our discussion breaks down as follows:
1. What Is Business?
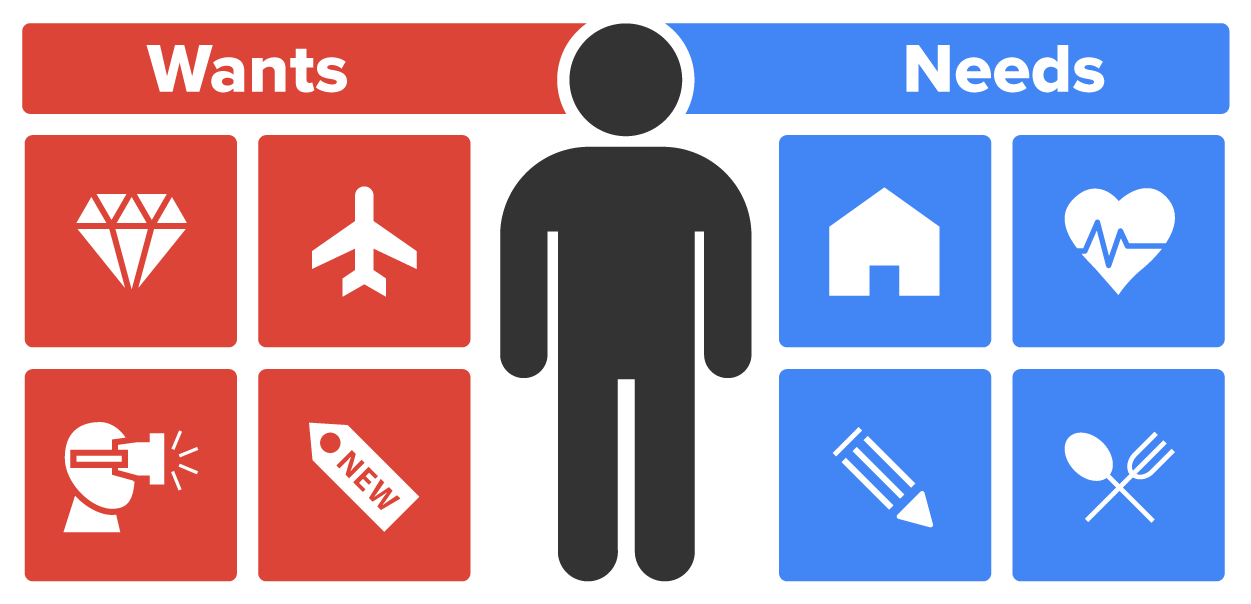
A business is simply an organization that attempts to earn a profit through the sale of goods or services. Those goods or services can be practically anything you can think of, but what they all have in common is that they fulfill a need or a want in our everyday life.
-
EXAMPLE
Needs may include things like food, clothing, or shelter. Wants, on the other hand, could be something like the brand-new Sea-Doo or the latest model car or electronic device—things that we don’t necessarily need to survive, but we want.
-
- Business
- An organization that attempts to earn a profit through the sale of goods or services.
1a. What Do Businesses Do?
Businesses help do several things that add value to individuals’ lives and to society as a whole. This includes the following:
- They improve our quality of life by fulfilling our wants and needs and by providing goods and services that we consume every day.
- They provide a choice for what it is we want to buy. Do we want to buy a Mac, for example, or do we want to buy a PC?
- They provide opportunities with the wide array of products that we have to choose from—not only for us as consumers but also for new start-up companies to enter the market and exploit a niche in the market or a gap in those wants and needs that they see. They also provide opportunities for jobs for people like you and me.
1b. Why Study Business?
What is important about business? Well, the study of business impacts your job and your job search, regardless of the field that you’re in. Understanding what’s going on around you and the terminology of business not only helps you to be a better employee but also helps make you a more valuable and sought-after employee.
-
It also helps you to be a better consumer. Understanding the terminology of business can help you understand, for example, if you are getting a good deal on a loan or not.
1c. Profits Versus Losses
Two important aspects of all businesses are profits and losses.
-
Profit: This is what remains after all business expenses have been deducted. In order to continue, a business must be able to make money or create something of equivalent value for its owners and investors.
-
Loss: This is when expenses become larger or greater than sales or revenue.
Profits are always good. Losses, as you can probably guess, are not. A profit means you’re successful, and you’re able to pay your employees, grow your business, and stay in business. A loss means you may not be in business for very much longer.
-
- Profit
- When revenue and sales are greater than expenses, there is a profit.
- Loss
- When expenses are greater than sales, there is a loss.
2. The Free Enterprise System
The free enterprise system is defined as a market system with little control and regulation of the business by the government. In this capitalistic system, consumers are free to choose what products they want to buy, what wants or needs they want to fulfill, how they want to fulfill them, and how much they want to pay for those services.
By doing this, they help guide something called the “invisible hand.” Now, the invisible hand was an idea that was first introduced by a man named Adam Smith in his famous book The Wealth of Nations.
By “invisible hand,” we refer to the hand that guides the market in a free enterprise or capitalistic system. There’s no central authority or central planning that tells the market what it produces, where it sells it, and how much it sells it for. The consumers and businesses make that choice based on signals that they get from each other.
IN CONTEXT
Take the humble pencil, for example. Think about what it takes to make a simple pencil and put it in your hand.
You have to find the wood and graphite lead as well as the rubber and metal for the erasers. You have to find places to process all of those things—to manufacture, deliver, and sell them. Then, you have to have all the support that goes along with all those employees for each individual business.
All of this happens without any central authority dictating what to do. It’s pretty amazing if you think about it.
-
- Free Enterprise System
- A market system with little control and regulation of business (by the government).
3. Basic Economics of Business
When discussing the basic economics of business, the first thing we want to look at is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics.
Microeconomics is an area of economic study that focuses on specific markets, choices, and behaviors that affect price, cost, and demand.
-
EXAMPLE
Think of microeconomics as that individual transaction you have with an everyday business. It refers to small things, such as how much can a business charge before the consumer stops buying? How much is a consumer willing to pay? How much of something will they want to buy, and how often will they come back to buy it?
Macroeconomics, on the other hand, is a wider field of study. It’s an area of study that focuses on the impact of variables on economic infrastructure in its entirety. This can be on a regional, national, or global level.
-
EXAMPLE
If you listen to business news, you’ll hear references to terms and phrases like the consumer price index, coverage of what the market’s doing, or what the Federal Reserve (Fed) wants to do with interest rates by increasing or decreasing the amount of available money in the market. These are all things that have to do with the economy of the United States as a whole, and that is the macroeconomic view or larger picture.

-
- Microeconomics
- An area of economic study that focuses on specific markets, choices, and behaviors that affect price, cost, and demand.
4. Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship tends to attract highly creative, growth- and expansion-focused people. These people help fill the market’s unfilled needs and wants. They help drive that “invisible hand” that we were talking about earlier.
An entrepreneur is a person who pursues a business venture with growth and expansion as a primary goal.
-
Just starting a business doesn’t necessarily mean you’re an entrepreneur. Growth and expansion are going to be some of your primary goals in order for you to be called an entrepreneur by this definition.
Consider the following examples of entrepreneurship.
-
EXAMPLE
Entrepreneur: Levi Strauss
Business: Levi Strauss and Company
Levi Strauss partnered with a man called Jacob Davis to start Levi Strauss and Company. They identified a need at the time, and they helped fill that need.
Workers back in the late 1800s were going through clothes very rapidly. The clothes kept ripping and tearing, and they used denim to patch those holes. First, they created a set of coveralls. Then, they created a set of jeans that lasted much, much longer. They filled that need to have durable clothing. Over time, the company has grown not only to provide a need—clothing—but also to provide a want, like those 501s that consumers want to have.
-
EXAMPLE
Entrepreneur: Arianna Huffington
Business: Huffington Post
Arianna Huffington found a niche in the market. In this case, the gap in the marketplace that she found stemmed from the fact that the
Drudge Report was wildly popular, but there wasn’t a liberal version of it to report that side of the news. Therefore, that’s what the
Huffington Post became. It focused on daily trends in the news.
The
Huffington Post team didn’t worry about how many articles they had, necessarily; they simply put their resources into all of them. What they found was that they were getting home runs every once in a while. They didn’t worry as much about the misses because the home runs were what established the organization’s name. Basically, they found something that worked, and they put resources into it.
-
- Entrepreneur
- A person who pursues a business venture with growth and expansion as primary goals.
Today, we looked at what business is. We defined the term “business,” including what it does and why we study it. We learned about the dynamics of profit and loss as well as the free enterprise system. We learned about the basic economics of business, discussing the microeconomic and macroeconomic views of the economy in general. Lastly, we learned about entrepreneurship, which is shown by highly creative people who are growth-focused and fill gaps in the market to help drive the “invisible hand.”
Good luck!

