Table of Contents |
Web design is the process of creating the visual and functional aspects of websites. It involves planning and arranging content in a way that is both aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly. This includes selecting colors, fonts, graphics, and layouts to ensure the website is attractive and easy to navigate. Web design also focuses on the user experience (UX), ensuring that visitors can easily find the information they need and interact with the site effectively.
A well-designed website is not only visually appealing but also responsive, meaning it adapts to different screen sizes and devices, such as smartphones and tablets. This ensures a consistent and accessible experience for all users. Web designers often use coding languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build and style websites, and they may collaborate with other professionals, such as UX designers and developers, to create a cohesive and functional site. A web coding language, also known as a web programming language, is used to create and manage the content, structure, and functionality of websites. For a designer to begin creating for the web, he or she must have an understanding of the client-server model and a working knowledge of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript language.
The client-server model is fundamental to how websites function. It involves communication between different devices classified as either clients or servers. It is a network architecture where a server provides resources or services, and clients request and use them. A client is any device used to access a website, including computers, smartphones, tablets, and gaming consoles. A server is a computer that hosts a website. An easy way to remember this is that the server serves the website to the client much like a waiter in a restaurant serves food to the patrons who order it. Note that any computer can be a server by installing server software and ensuring that the computer is powered on and constantly connected to the internet. Server software is designed to manage, run, and operate a computer server. It enables the server to provide various services and functionalities to connected clients or end users. This software harnesses the server’s computing power to handle tasks such as data storage, communication, and application hosting.
Web hosting is a service that allows individuals and organizations to make their websites accessible on the internet. When you purchase a web hosting plan, you are essentially renting space on a server where all the files and data for your website are stored. This server is maintained by a web hosting provider, which ensures that your website is available to visitors around the clock.
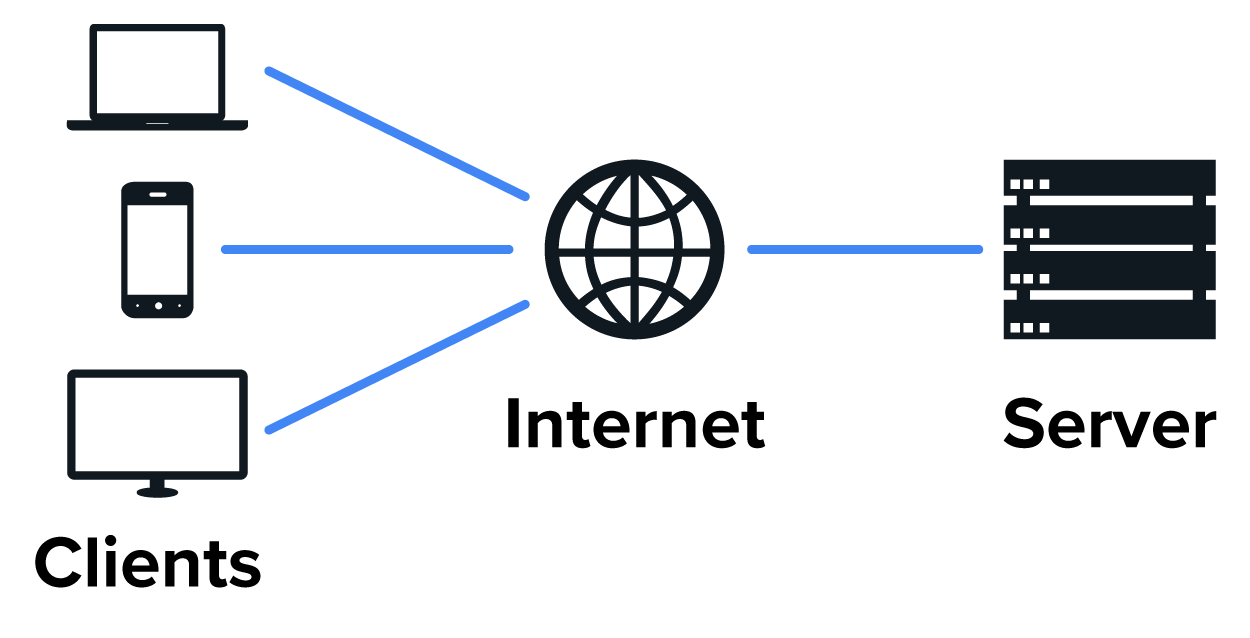
When a user accesses a website, the web browser on their device sends a request to a web server, which hosts the website’s files and data. A web browser is a software application used to access and view websites on the internet. The server processes this request and sends back the necessary resources, such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, which the browser then renders into the web page the user sees. This interaction follows a request-response pattern, where the client initiates communication and the server responds with the requested information. This model allows for efficient management of web resources, enabling servers to handle multiple client requests simultaneously. It also centralizes control, making it easier to update and secure web content.
Websites are collections of documents and other content organized in folders. These folders and the content within them are stored on server computers, sometimes called remote servers or remote hosts. When a client device searches for a website, the device seeks out the Uniform Resource Locator, or URL. A URL is the address used to access resources on the internet, such as web pages, images, or files, specifying the location and the protocol used to retrieve them. To better understand URLs, think about a website as if it were an actual place you wanted to visit, like a store. To get to the store, you need to travel to its physical address. The URL is an address in cyberspace. By directing a browser to go to it, the browser can access the server computer and open the folder housing the website’s files.
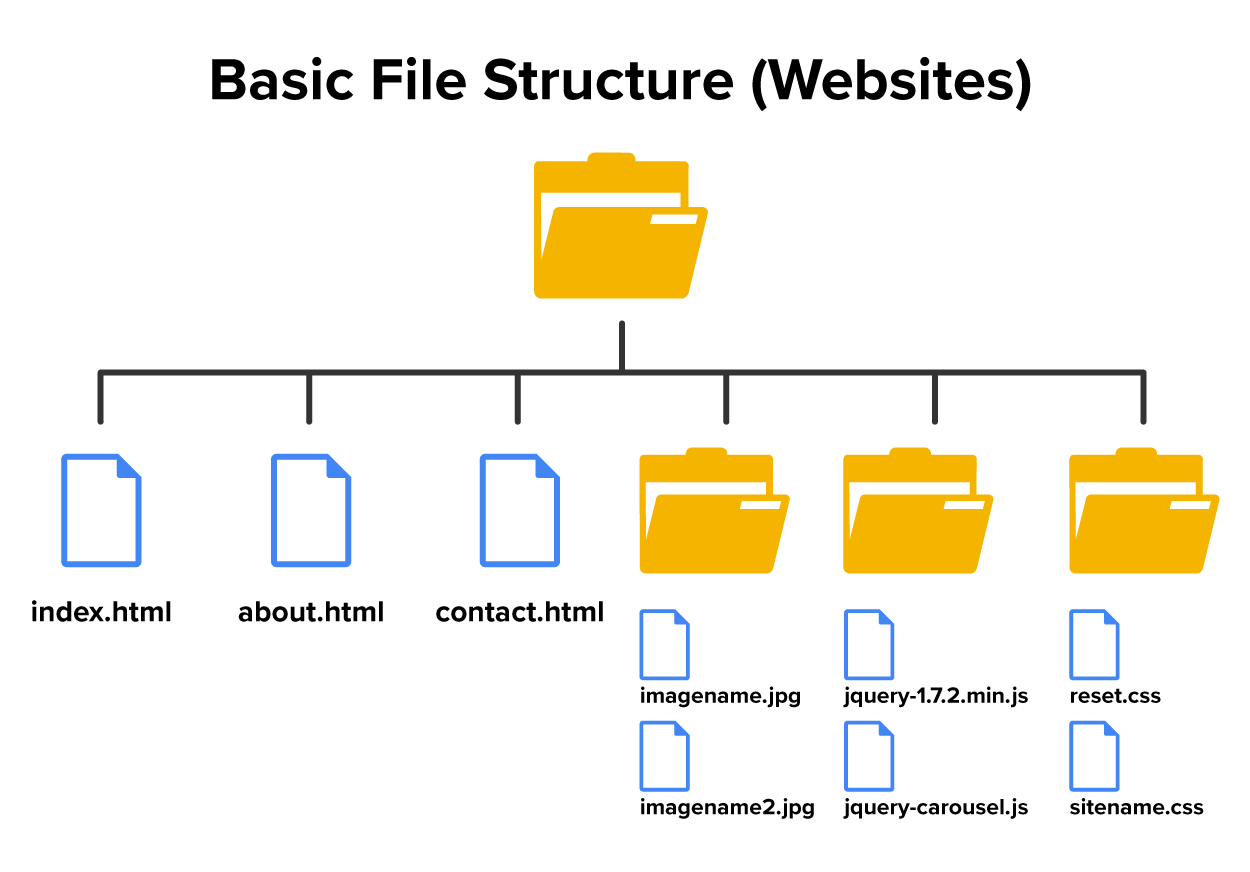
Generally, a website will consist of a main folder or directory called a root folder, with additional subfolders and files nested within it. A very simple website may only use a root folder and one subfolder to contain images, while other websites may use multiple folders to make up their file structure. File structure refers to the organized hierarchy of folders and files that make up a website, ensuring that all elements like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and media files are systematically arranged for easy access and maintenance. Depending on the size and functionality of the website, the file structure may increase in complexity, adding more folders to categorize different file types and media.
In the example below, the root folder contains three subfolders: images, js (for JavaScript), and css. Three HTML files are nested directly in the root folder. Note that all of the files and directories are named in lowercase letters with no spaces or special characters in between. All websites should follow this type of naming convention to ensure that clients and servers can successfully serve and retrieve files. A naming convention is a set of agreed-upon rules and guidelines for naming things in a consistent and organized manner, often used to improve clarity, readability, and maintainability in various fields like programming, data management, and documentation.
When a website is visited, the client device’s browser accesses the internet and then searches for the URL. The components of the URL define the protocol, subdomain, second-level domain, and top-level domain.
A protocol is a set of rules and conventions that determine how data is transmitted and received over a network, ensuring proper communication between devices. Think of protocols as the rules of the road for the internet. Just like traffic rules help cars navigate safely and efficiently, protocols help computers and devices communicate with each other smoothly. HTTP, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is the communication standard that web browsers and servers use to exchange information. When you enter a web address or click on a link, HTTP facilitates the request from your browser to the server and ensures the web page is delivered back to you. It is the fundamental protocol that enables the functioning of the World Wide Web. A domain is a unique address on the internet where a website can be found. It serves as the online identity for a website, making it easier for users to access and remember. A subdomain is a part of a larger domain name, used to organize and separate different sections of a website.

A second-level domain (SLD) is the part of a domain name that appears directly to the left of the top-level domain (TLD). Note that not all URLs contain second-level domains. A top-level domain (TLD) is the last part of a domain name, appearing after the final dot. Top-level domains categorize websites based on their purpose or geographic location. For example, .com is intended for commercial businesses, .org for non-profit organizations, .edu for educational institutions, .gov for government entities, and .uk for websites from the United Kingdom. There are many other choices for top-level domain names depending on the nature of the website and the country it is based in.
HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language and is the dominant programming language for producing content on the web. It uses a system of tags and attributes to define the elements on a page, such as headings, paragraphs, links, images, and other multimedia. HTML tags are the building blocks of a web page. They are used to mark up and define the structure of the content within the HTML document. HTML tags are enclosed in angle brackets and typically come in pairs, with an opening tag and a closing tag.
Each HTML document is essentially a set of instructions that tells a web browser to display content. HTML provides the basic structure of a web page, organizing content into elements like headings, paragraphs, and lists. It allows for the inclusion of images, audio, video, and other multimedia elements, making web pages more engaging and interactive. HTML enables the creation of hyperlinks, which connect different web pages and resources, facilitating easy navigation across the web. A hyperlink, often simply called a link, is a reference in a digital document that a user can click or tap to navigate to another location or file. Hyperlinks are commonly used in web pages to connect different sections of the same document or to link to entirely different documents or websites. A hyperlink that connects to other pages or files contained in the same site is called a relative hyperlink, whereas a hyperlink that connects to an external resource, such as another website or file located on another server is called an absolute hyperlink. Hyperlinks can be embedded in text, images, or other elements, making them interactive and easy to use. For example, in a web page, a hyperlink might appear as underlined or colored text. Clicking on it allows the web browser to access the linked page or resource. This functionality is fundamental to the web, enabling seamless navigation and access to a vast array of information. Remember that HTML deals with the content of web pages.
CSS, or Cascading Style Sheets, is a language used to style and lay out web pages, allowing users to control the appearance of HTML elements, such as colors, fonts, and spacing. There are three main types of CSS: inline CSS, where styles are applied directly within an HTML element; internal CSS, where styles are defined within a tag in a specific section of an HTML document, which is useful for applying styles to a single page; and external CSS, where styles are written in a separate .css file and linked to the HTML document using a special tag. External CSS is ideal for applying consistent styles across multiple pages.
The term “Cascading Style Sheet” comes from the coding language's ability to cascade or flow style changes throughout a document. Web designers can easily edit or even change out entire CSS files and apply massive changes to a website’s appearance with minimal time and effort. CSS works by linking to the HTML documents in a website and telling the browser how to display the content in specified HTML tags. CSS can change the color, size, and typeface of text, create multicolumn designs, positioning elements precisely and ensuring that layouts adapt to different screen sizes, adjust the spacing between elements, such as margins and padding, and set background colors, resize and position images, and apply gradients. CSS can also be used to define the style, width, and color of borders, add shadows to elements, and create simple animations.
Remember that HTML handles the content of a website, whereas CSS controls the appearance of that content. HTML and CSS are both languages for web design, but they are used for different purposes. HTML is used to build structural layers, while CSS is used for the presentation of those layers.
You can think of HTML as the structure of a house and CSS as the decorations that make it look nice. Below are basic examples of HTML and CSS code.
JavaScript is a programming language that makes web pages interactive. It’s one of the main tools used on the web, along with HTML and CSS. With JavaScript, users can create features that update automatically, control videos and images, and respond to user actions like clicks and form submissions.
JavaScript can be used in different ways, like handling events, writing functions, and creating objects. Events are actions or occurrences that happen in the browser, which the browser can detect and respond to. These events can be triggered by user interactions, such as clicking a button, typing in a text field, or moving the mouse over an element. They can also be system-generated, like when a web page finishes loading or a video ends. When an event occurs, it can be handled by an event handler, which is a function that executes in response to the event. For example, you might have a button that changes color when clicked. The click event triggers a function that changes the button’s color. Functions are blocks of code designed to perform a particular task. They help in organizing code, making it reusable, and improving readability. For example, you might have a function that calculates the sum of two numbers. You can call this function whenever you need to perform that calculation, rather than writing the same code multiple times.
Where HTML controls the content of websites and CSS manages their appearance, JavaScript controls functionality.
Web design in practice involves creating visually appealing and user-friendly websites by combining aesthetics and functionality. It includes arranging content in a logical layout, selecting a cohesive color scheme, and choosing fonts that enhance readability. Graphics and images are used to make the site more engaging. Responsive design ensures the site works well on various devices, and accessibility features make it usable for people with disabilities. Web design is a collaborative effort involving designers, developers, and content creators working together to create a cohesive and functional website. Additionally, web designers must stay updated with the latest trends and technologies to ensure the website remains modern and competitive. This includes incorporating animations, optimizing load times, and ensuring cross-browser compatibility. Effective web design also involves regular testing and feedback to continuously improve the site’s performance and user satisfaction.
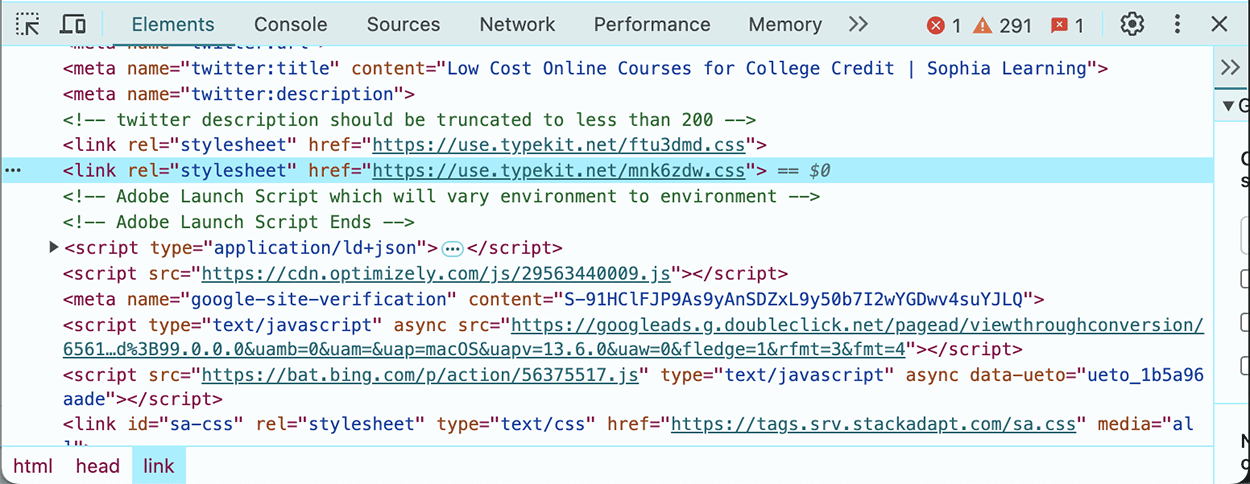
A good way to become familiar with web design is to explore the coding of existing websites. Most browsers allow users to view the source code of a web page, showing the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files used to generate the content, appearance, and functionality of pages.
In the example above, you can see the HTML code at the bottom; everything is encapsulated in this box from top to bottom.
There's CSS in there as well, indicated by the style syntax. HTML and CSS live together in the same source code.
Responsive web design is an approach to creating websites that ensures they look and function well on a variety of devices and screen sizes, from mobile phones to desktop monitors. Responsive web design makes sure websites work well on all devices, from phones to computers. It aims to give users a good experience by making sites easy to read and navigate without needing to zoom in or scroll too much. This is done by using flexible layouts that adjust to different screen sizes, images that resize to fit, and special CSS rules that change styles based on the device. This approach improves user satisfaction, saves money by avoiding the need for multiple site versions, boosts search engine rankings, and keeps sites future-proof. Additionally, responsive design ensures that websites remain accessible and functional as new devices with varying screen sizes and resolutions are introduced, providing a consistent and enjoyable user experience across all platforms.
Good web design offers numerous benefits that can significantly impact the success of a website and the business it represents. It creates a positive first impression. An intuitive, attractive, and professional-looking website tells new visitors that a company is customer-focused and forward-thinking. This can help establish trust and credibility right from the start.
Effective web design improves SEO (Search Engine Optimization). SEO is the process of enhancing a website to improve its visibility in search engine results. A well-structured and optimized website is more likely to rank higher in search engine results, making it easier for potential customers to find. This increased visibility can lead to more traffic and higher conversion rates. A conversion rate is a metric used in digital marketing to measure the percentage of users who complete a desired action out of the total number of visitors to a website or marketing platform. This desired action, known as a conversion, can vary depending on the goals of the business. Common examples of conversions include making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, filling out a contact form, or downloading a resource.
Additionally, good web design enhances user experience by providing easy navigation, faster load times, and accessibility features. This ensures that visitors can find what they need quickly and easily, which can keep them on your site longer and encourage them to return.
Moreover, a well-designed website can give a business a competitive advantage. In a crowded market, a unique and modern website can help a brand stand out and attract more customers. Good web design also builds trust and credibility. A professional and error-free website signals to visitors that a business is reliable and trustworthy, which can increase the likelihood of them becoming loyal customers.
Source: THIS WORK IS ADAPTED FROM SOPHIA AUTHOR MARIO E. HERNANDEZ