Table of Contents |
This lesson builds upon what we learned earlier about using inverse operations to isolate the variable, applying this knowledge to equations requiring two steps to solve for the unknown value. Remember, when solving an equation for a variable, our main goal is to isolate a variable. In other words, we want to get the variable by itself on one side of the equation, with all other expressions on the other side of the equals sign. In this process, we must always remember that if we perform an operation on one side of the equation, we must do the same on the other side of the equal sign. Let's look at an example:
EXAMPLE
Solve for x in the equation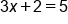
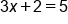
|
The equation. |
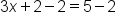
|
You could divide every value by 3 or subtract 2 from both sides. If you divide everything by 3 first, you'll end up with fractions (or decimals), which would make it more challenging for the next step. Let's take the easiest option and subtract 2 from both sides. |
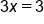
|
The constant is now removed from the left side. |
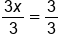
|
To isolate x, Divide both sides by 3. |
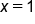
|
On the left side, the variable is isolated, and the solution is x = 1. |
EXAMPLE
Solve for x in the equation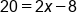 .
.
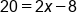
|
The equation |
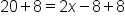
|
Again, let's get rid of the value not touching the variable. So, add 8 to both sides because it is the opposite of subtraction. |
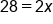
|
The constant is now removed from the right side. |
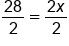
|
Divide both sides by 2 because it is the opposite of multiplication. |
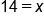
|
On the right side, the variable is isolated, and the solution is x = 14. |
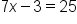 .
.
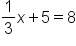 .
.
When working with word problems, it is always a good idea to start by clearly labeling the variables in a short list before we begin to solve the problem. This is important in all word problems involving variables, not just consecutive numbers or geometry problems.
IN CONTEXT
Speedy Taxi company charges $5 for the initial pick up and then $2/mile. If you spent $33, how many miles did you travel?
First, establish the variable: x = miles traveled
Now set up your equation.


The equation. 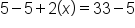
To solve for x, first subtract 5 from both sides because it is the opposite of addition (or, in this case, a positive number). 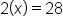
The constant is now removed from the left side. 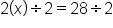
Divide both sides by 2 because it is the opposite of multiplication. 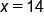
On the left side, the variable is isolated, and the solution is x = 14.
You traveled 14 miles.
IN CONTEXT
A sofa and a loveseat together costs $444. The sofa costs double the loveseat. How much do they each cost?
First, establish the variable. With no information about the loveseat, this is our x: Loveseat = x.
The sofa is double the loveseat, so we multiply by x by 2 to represent the cost of the loveseat. Together, they cost $444, so we add x and 2x and create the following equation to solve:
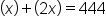
The equation 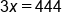
Parentheses are not needed; combine like terms x and 2x. 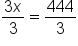
Divide both sides by 3. 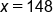
On the left side, the variable is isolated, and the solution is x = 148.
The love seat costs $148, which means the sofa costs twice as much, or 2($148) = $296.
Problem Solving: Skill Tip |
Source: THIS TUTORIAL WAS AUTHORED BY SOPHIA LEARNING. PLEASE SEE OUR TERMS OF USE.