Table of Contents |
Companies develop a marketing strategy, an approach to achieving a specific objective or goal, to direct their product design, pricing, promotion, and distribution. This strategy requires creating an overall plan and timeline, analyzing the market and data, implementing a campaign, and adjusting their activities based on analytics. A marketing strategy is the plan to reach customers and convert them into loyal buyers of the brand.
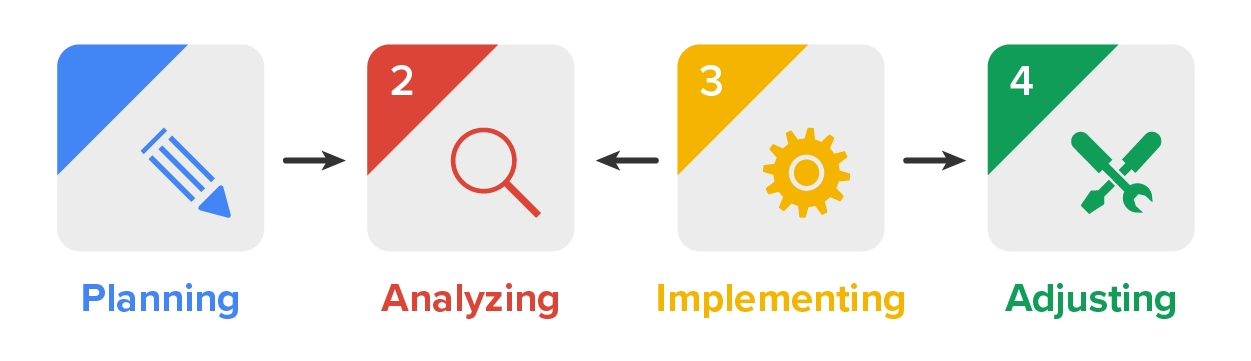
The process of creating a marketing strategy begins with a plan—an organized approach to a market. At this stage, marketers work to develop the objectives for a marketing campaign (or series of messages and experiences). An objective is the longer-term goal that a company wants to achieve with a specific customer group. Each action that a marketer performs needs to align with this overall objective. The objective should be SMART or specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and defined for a period of time.
Once a marketing team has defined its objective, it needs to analyze the market. The focus should be on its customer groups to learn what buyers think about existing products and what they would like to see in future offerings. The marketing team will analyze, which means to review and evaluate the data from customers to determine the company’s unique approach, design, and messaging for a campaign. Marketers will also analyze data about competitors to create the most compelling experience possible for customers.
After analyzing the customer data, marketers will implement their campaign. This means crafting the messaging, designing visual elements, choosing the media and outlets they will use, engaging with customers and influencers online, and using every opportunity to ensure that the market is aware of their offering. Social listening is important at this stage, which means observing customer behavior and communication to determine the effectiveness of the campaign.
Campaign implementation requires adjusting the marketing activities to ensure that a company is achieving its defined objective. If customers are responding favorably to a campaign, sharing the content with friends, and providing feedback that is useful to marketers, the campaign can be improved by reaching more customers. If customers are not posting, not sharing, and not engaging with the content or not buying the product, this is also useful because the company can adjust its product or message to increase sales.
The marketing process (an approach to achieving a specific objective or goal, to direct product design, pricing, promotion, and distribution) supports a company’s marketing strategy.
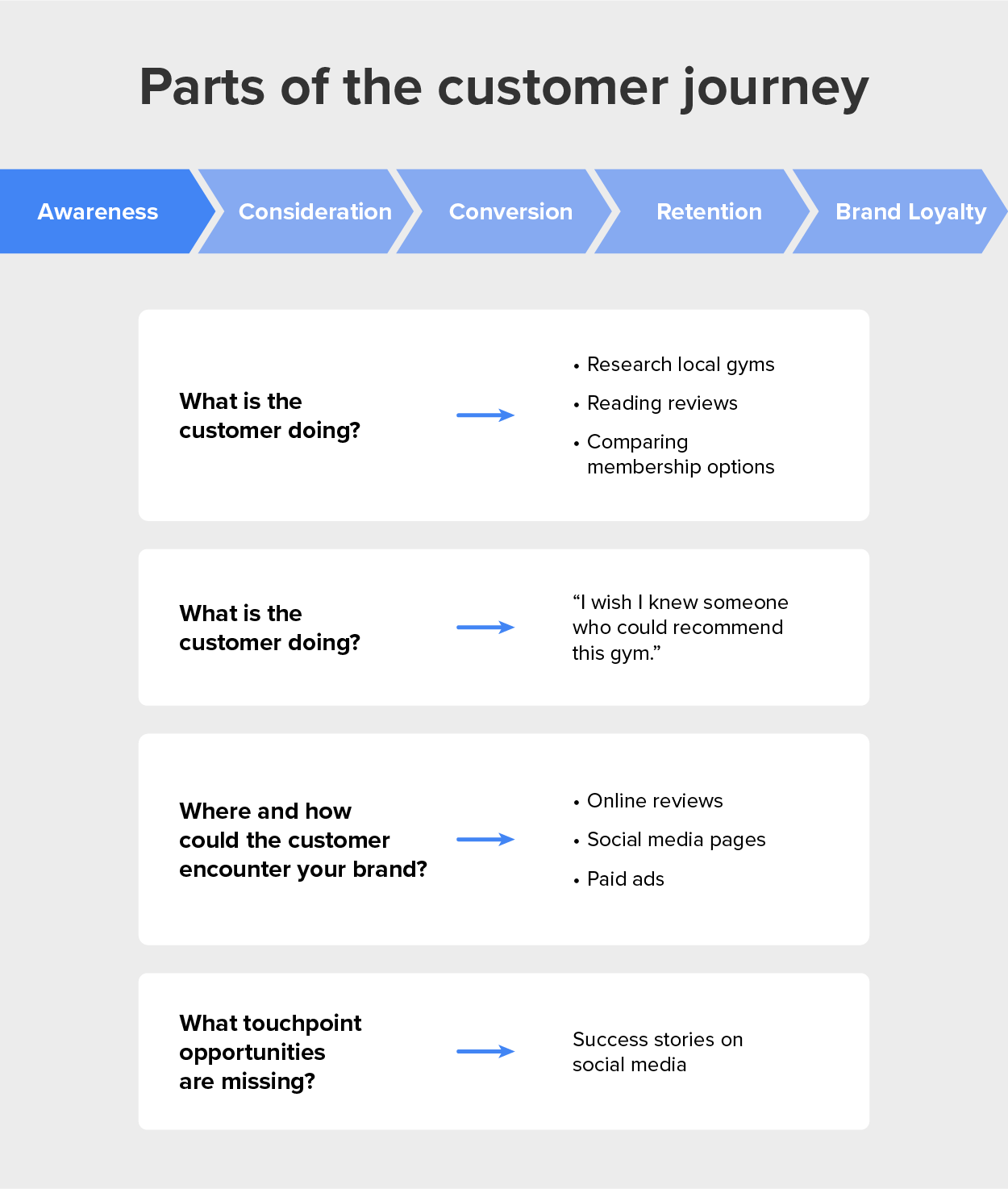
Marketers need to understand their customers and know exactly where their products fit into buyers’ lives. One way to do this is by developing a customer journey map that identifies what a typical buyer’s experience is with the product, from the point at which a customer decides they want to improve their lives to the time when they buy the company’s product and refer the brand to their friends. Marketers also need to understand how much customers are willing to pay for a product, what influences their purchases, and from where they purchase their favorite brands.
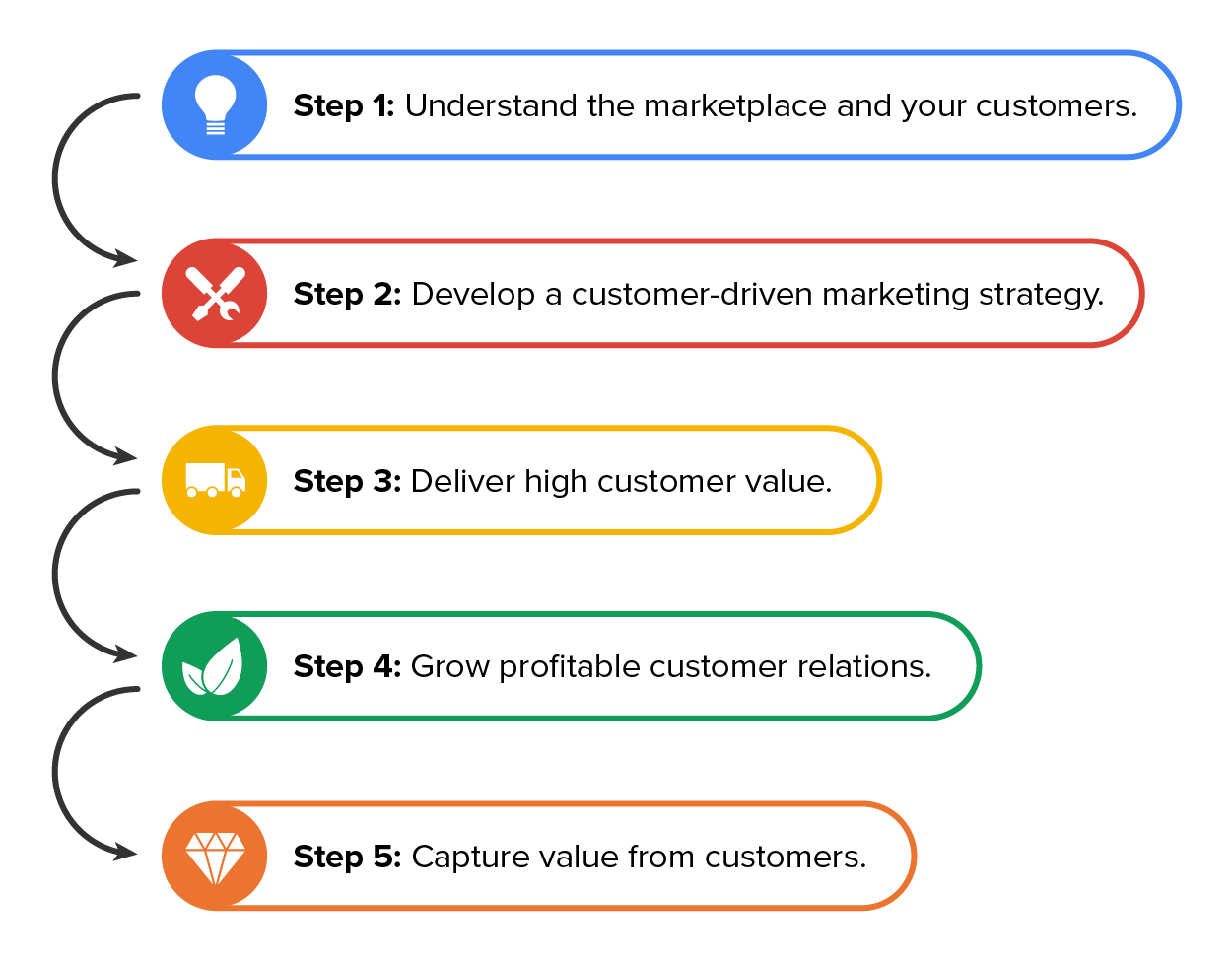
Once companies know and understand their buyers, they need to develop a customer-focused marketing strategy. A marketing strategy is the plan to reach customers and convert them into loyal buyers of the brand. A customer-focused marketing strategy means that a company considers every aspect of its product through the lens of its customers. Important to this is ensuring that marketers focus on diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging (DEIB) in every aspect of their experiences. Diversity is acknowledging the variety and vast differences between individuals, while inclusion focuses on ensuring that each is recognized for their unique value to the brand. Equity focuses on ensuring that every person has equal access to the same experience and value offered by a company, while belonging requires companies to create an environment where people’s unique values and perspectives are intentionally welcomed. Marketers must demonstrate that their products deliver unique value that is recognized as being different from competitive products through a value proposition that defines what the product will do for the customer.
Marketers need to understand their customers and know exactly where their products fit into buyers’ lives.
IN CONTEXT
One way to do this is by developing a customer journey map that identifies what a typical buyer’s experience is with the product, from the point at which a customer decides they want to improve their lives to the time when they buy the company’s product and refer the brand to their friends.
Marketers also need to understand how much customers are willing to pay for a product, what influences their purchases, and from where they purchase their favorite brands.
Companies need to build profitable relationships that increase customer share of wallet, which is the amount each customer spends on products. As customers increasingly trust that companies care about their needs and wants and design products, services, and experiences to meet their expectations, they spend more of their incomes on those brands.
Customers exchange their money for goods and services. This exchange creates value for the companies that design, price, promote, and deliver those products in the form of profits. Equally important are insights customers provide to marketers that help the company anticipate future product opportunities, threats from competitors, and trends in the marketplace.
Source: THIS TUTORIAL HAS BEEN ADAPTED FROM OPEN STAX’S PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING COURSE. ACCESS FOR FREE AT https://openstax.org/details/books/principles-marketing. LICENSE: CREATIVE COMMONS ATTRIBUTION 4.0 INTERNATIONAL.
REFERENCES
Pell, A. (2023). Customer Journey Mapping 101 (+ Free Templates). Retrieved from zapier.com/blog/customer-journey-mapping/