Table of Contents |
The selection process is the part of hiring that focuses on identifying the best candidate for a role.
The process starts with screening applications, where HR professionals sift through resumes and cover letters to find those who meet the job’s basic requirements. This step helps narrow down the pool to the most promising candidates.
After screening, the interview process assesses a candidate’s fit with the company’s culture and values. Interviews can be conducted over the phone, via video, or in person, each offering unique insights. During these interviews, questions are designed to evaluate the candidate’s skills, experience, and personality. Behavioral questions are valuable as they reveal how candidates have handled past situations, offering a glimpse into their future performance.
Beyond interviews, additional assessments such as tests, simulations, and reference checks may be employed. Tests can gauge technical skills, cognitive abilities, or personality traits, while simulations allow candidates to demonstrate their capabilities in a controlled setting. Reference checks involve contacting previous employers to verify the candidate’s work history and performance, providing a fuller picture of their suitability.
After gathering all this information, HR professionals and hiring managers review and compare it against the job requirements. They consider factors like skills, experience, cultural fit, and potential for growth. The goal is to select the candidate who best aligns with the role and the company’s needs.
Screening candidates is where the company sifts through applications to identify the most suitable individuals for a job. This process helps ensure that only the best candidates move forward to the next stages, such as interviews. It involves evaluating resumes, cover letters, and sometimes initial assessments or questionnaires.
Screening candidates often include phone screens, video interviews, and in-person interviews. These steps help further evaluate a candidate’s suitability for the role and fit within the company culture.
The goal of screening is to match applicants' qualifications and experiences with the job's requirements. This means looking at their education, work history, skills, and sometimes even their personal attributes. It’s about finding a good fit between what the job demands and what the candidate offers.
One of the first steps in the screening process is to check if the candidate meets the basic qualifications. This might include specific degrees, certifications, or a certain amount of experience. If they don’t meet these criteria, they are usually not considered further. This helps narrow down the pool of applicants to those who are more likely to succeed in the role.
Next, look at the quality of their experience and skills. This involves a more detailed review of their resume and cover letter. You might look for specific achievements, relevant projects, or skills that stand out. This step helps identify candidates who not only meet the basic qualifications but also bring something extra to the table.
Sometimes, screening also includes initial assessments or tests. These can help gauge a candidate’s abilities or fit for the company culture. However, these are usually just one part of the overall screening process.
Pre-employment tests are designed to assess the abilities, skills, and fit of potential candidates before making a job offer. These tests can take various forms, including cognitive ability tests, personality assessments, skills tests, and situational judgment tests. Each type of test serves a specific purpose and provides insights that are not always apparent from resumes or interviews alone.
| Cognitive Ability Tests | Measure a candidate’s general mental capacity, including reasoning, memory, and problem-solving skills. These tests are often used to predict job performance and the ability to learn new tasks. They can be particularly useful for roles that require strong analytical thinking or complex decision-making. |
| Personality Assessment | Evaluate traits such as extroversion, conscientiousness, and emotional stability. These tests help determine how well a candidate’s personality aligns with the company culture and the specific demands of the job. For example, a role that requires teamwork and collaboration might benefit from candidates who score high on agreeableness and openness. |
| Skills Tests | Designed to measure specific job-related abilities. These can range from typing tests for administrative positions to coding challenges for software developers. By assessing these skills directly, employers can ensure that candidates have the necessary competencies to perform the job effectively. |
| Situational Judgement Tests | Presents candidates with hypothetical scenarios related to the job and asks them to choose the best course of action. These tests assess decision-making, problem-solving, and interpersonal skills. They provide a glimpse into how candidates might handle real-life situations they could encounter in the workplace. |
Pre-employment testing offers a structured and objective way to evaluate candidates, reducing the risk of bias and improving the chances of hiring the right person for the job. By incorporating these tests into the hiring process, organizations can make more informed decisions and build a stronger, more capable workforce.
Assessment centers are used in hiring to evaluate candidates through various exercises and simulations. Unlike regular interviews, assessment centers offer a more interactive way to see if someone is right for the job. They include activities like group discussions, role-playing, case studies, and presentations, all designed to reflect real job scenarios. This allows candidates to show their skills in a practical setting.
For instance, in hiring for customer service roles, assessment centers might include activities like handling mock customer complaints, participating in team problem-solving exercises, and conducting simulated phone calls. These tasks help employers see how candidates manage real-life customer interactions, demonstrating their communication skills, problem-solving abilities, and teamwork in a practical environment.
One major benefit of assessment centers is that they provide a complete picture of a candidate’s abilities. By watching candidates in different situations, employers can understand their problem-solving skills, teamwork, leadership potential, and communication abilities. This approach helps make the selection process fairer and more objective, reducing the chance of bias that can happen with traditional interviews.
Assessment centers are especially useful for jobs that need strong interpersonal skills or leadership qualities. For instance, management roles often use this method to see how candidates handle complex situations and interact with others. The feedback from these exercises can also help candidates understand their strengths and areas where they can improve.
EXAMPLE
For a management position, an assessment center might use several tests. Candidates could participate in group discussions to show their teamwork and communication skills. Role-playing exercises might be used to see how they handle conflicts or lead a team. Case studies could test their problem-solving and decision-making abilities. Finally, presentations might be used to assess their ability to convey ideas clearly and persuasively. These tests help ensure the candidate has the right skills for the job.Reference checks provide insights into a candidate’s past performance and behavior, which can help predict their future success in your organization. When conducting reference checks, it’s important to speak with individuals who have directly supervised or worked closely with the candidate. These references can offer firsthand accounts of the candidate’s work ethic, reliability, and interpersonal skills.
During a reference check, you should ask open-ended questions that encourage detailed responses.
EXAMPLE
Instead of asking if the candidate was a good employee, you might ask the reference to describe a time when the candidate went above and beyond in their role.This approach can reveal more about the candidate’s strengths and areas for improvement.
It’s also essential to verify the accuracy of the information provided by the candidate. This includes confirming employment dates, job titles, and responsibilities. Discrepancies between the candidate’s resume and the reference’s account can be a red flag.
Remember, reference checks are not just about finding out if a candidate is qualified. They are also an opportunity to learn about the candidate’s fit within your company culture. By gathering comprehensive and honest feedback from references, you can make more informed hiring decisions and select candidates who will thrive in your organization.
Background screening is a process that can include checking for items such as criminal history, education, and credit reports. It’s essential to obtain the candidate’s permission before conducting these checks, as this is both a legal requirement and a matter of transparency and respect for the candidate’s privacy.
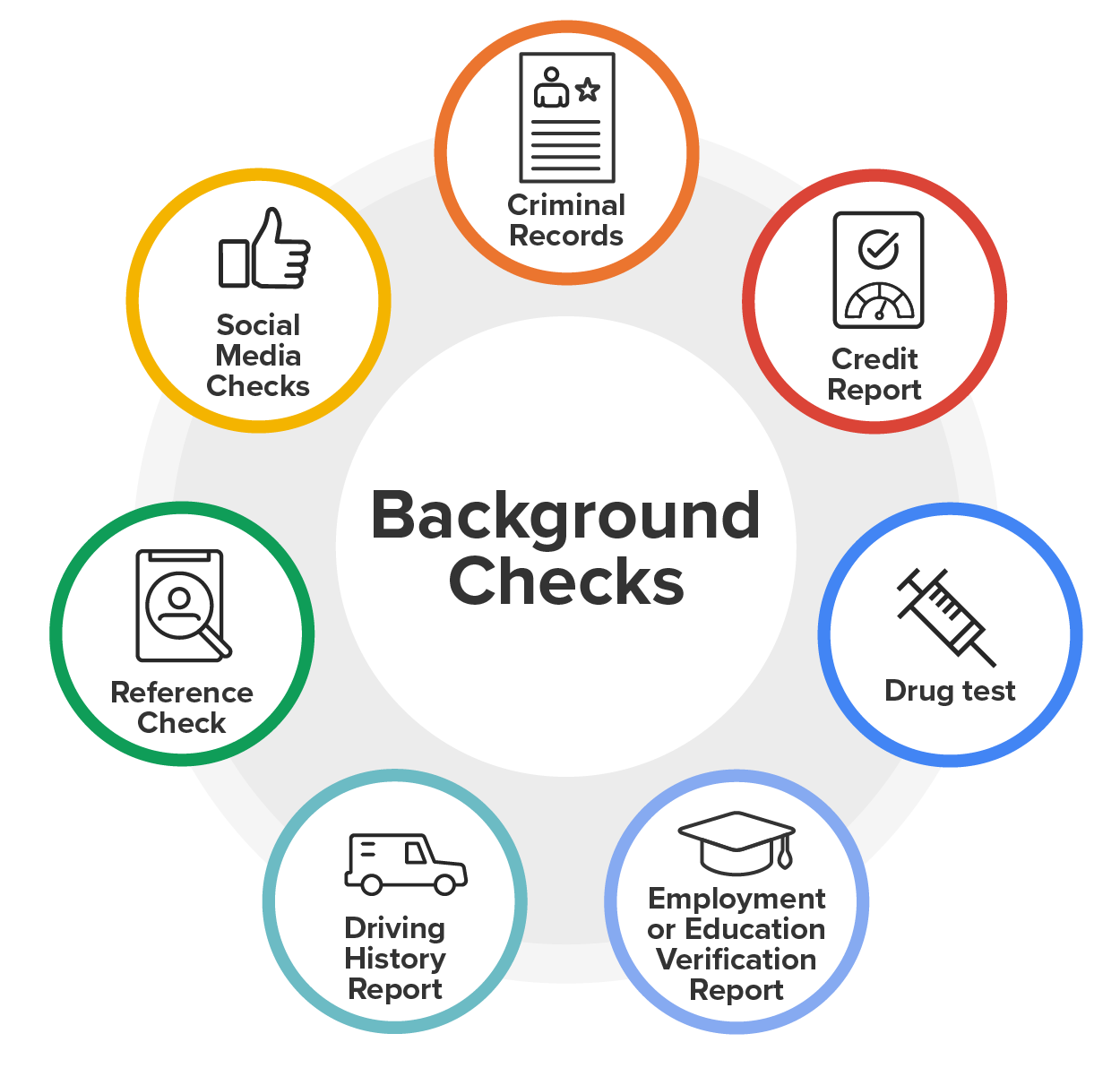
Reviewing a candidate’s criminal history helps identify any past behavior that might pose a risk to the organization or its employees. For example, a history of violent offenses or theft could be particularly worrying, depending on the nature of the job. However, it’s important to approach this information with a balanced perspective. Not all criminal records are equally relevant to all positions. For instance, a minor offense from many years ago may not be pertinent to a candidate’s current suitability, especially if they have demonstrated positive behavior since then.
Credit reports can provide insight into a candidate’s financial responsibility and may be particularly important for roles that involve financial management, handling sensitive information, or positions of trust. A poor credit history might indicate potential risks, such as financial stress or irresponsible behavior, which could impact job performance. However, as with criminal history, it’s crucial to consider the context. Financial difficulties can arise from various circumstances, and a single negative mark on a credit report doesn’t necessarily reflect a person’s overall character or ability to perform a job effectively.
If a background check reveals negative information, it’s important to handle the situation fairly and thoughtfully. Employers should consider the relevance of the findings to the job in question.
EXAMPLE
A candidate with a past misdemeanor unrelated to the job’s responsibilities might still be a strong candidate. Additionally, employers should provide candidates with an opportunity to explain any negative findings. This can offer valuable context and demonstrate the candidate’s honesty and willingness to address past issues.When conducting background screenings, it’s also important to be aware of and comply with relevant laws and regulations. Different jurisdictions have varying rules about what information can be considered and how it must be handled. For instance, as discussed previously, some areas have “ban the box” laws that restrict when and how employers can inquire about criminal history. Ensuring compliance with these regulations helps protect the organization from legal risks and promotes fair hiring practices.
Many organizations outsource background screening and hire outside experts to conduct the background check. This process can provide unbiased screenings while saving time and resources. It’s important to get the candidate’s consent and follow legal guidelines to stay transparent and respect privacy.
By conducting thorough background screenings and handling the results fairly, organizations can make more informed hiring decisions, reduce risks, and ensure a safer, more reliable workforce. This diligence helps protect the company’s reputation and fosters a secure working environment. Moreover, transparent and fair screening processes can enhance the candidate experience, demonstrating that the organization values integrity and fairness.
Making an offer is the moment when you formally invite a candidate to join your organization. This step requires careful preparation and clear communication to ensure the candidate feels valued and informed.
| Offer Letter | This document should include the job title, salary, benefits, and other relevant details. Clarity and transparency are essential to prevent any potential misunderstandings. |
| Candidate Communication | Once the offer letter is prepared, communicate the offer to the candidate. This can be done via email, phone call, or in person, depending on the company’s culture and the candidate’s preferences. During this interaction, convey enthusiasm and support to make the candidate feel welcomed and appreciated. |
| Consideration Time | Allow the candidate time to consider the offer. They may have questions or need to discuss it with their family. Be available to provide additional information and answer any queries they might have. |
| Onboarding | Upon acceptance of the offer, initiate the onboarding process to ensure a smooth transition into their new role. This step is crucial for setting the stage for the candidate’s success within the organization. |
Extending a job offer is not merely about filling a position; it is about establishing a positive relationship and laying the groundwork for a successful working experience
When making an offer, it is important to understand the employment relationship and clearly communicate this within the offer letter. There are two main types of employment relationships: at-will and contract.
At-will employment means that either the employer or the employee can end the employment relationship at any time, for any reason, or even for no reason at all, as long as it’s not illegal. This flexibility can be beneficial for both parties, but it also means there is less job security for the employee.
Contract employment involves a formal agreement between the employer and the employee. This contract outlines specific terms and conditions of employment, such as the duration of employment, job responsibilities, salary, and other benefits. Unlike at-will employment, contract employment provides more stability and security for the employee because the terms are legally binding. However, it also means that both parties are obligated to adhere to the contract terms, and breaking the contract can lead to legal consequences. It is recommended that employers work with their legal counsel in creating a contract as there are many missteps that can happen.
EXAMPLE
An employee at a retail store can be let go without notice if the store decides to downsize. Conversely, in a contract employment situation, a software developer might have a one-year contract specifying their role, salary, and benefits. If the company wants to terminate the developer before the contract ends, they must follow the terms outlined in the agreement, which might include severance pay or other conditions.When a company extends a job offer, it often includes a condition that the candidate must pass a post-offer physical. This step is crucial for ensuring that the candidate is physically capable of performing the job’s essential functions. These physicals are typically conducted by healthcare professionals and can include various tests, such as vision and hearing assessments, drug screenings, and physical fitness evaluations.
The primary goal of post-offer physicals is to protect both the employee and the employer. For the employee, it ensures that they are not placed in a position that could exacerbate any existing health issues or pose new risks. For the employer, it helps in reducing workplace injuries and associated costs, such as workers’ compensation claims.
It’s important to note that these physicals must comply with legal standards, including the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). This means that the tests must be relevant to the job and not discriminatory. Employers must also keep the results confidential and use them solely to determine the candidate’s ability to perform job-related tasks.
Employment authorization ensures that every new employee is legally permitted to work in the United States. This involves verifying both the identity and employment eligibility of each new hire. One of the primary tools used for this verification is the Form I-9, Employment Eligibility Verification.
The Form I-9, which is issued by the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), is a mandatory document that both employers and employees must complete. Employers are responsible for ensuring that the form is filled out correctly and that the necessary documents are provided. These documents can include a passport, driver’s license, or social security card, among others. The goal is to confirm that the employee is who they say they are and that they are authorized to work in the country.
In addition to the I-9 form, employers must also be aware of various work visas and green cards that authorize employment. Work visas, such as the H-1B for specialty occupations or the L-1 for intracompany transferees, allow foreign nationals to work in the U.S. for a specific period. Green cards, or Permanent Resident Cards, grant individuals the right to live and work in the U.S. indefinitely. These documents are crucial for verifying that an employee has the legal right to work in the country.
Employers must understand the significance of these documents. Not only are they legal requirements, but they also help protect the company from potential fines and legal issues. Properly managing employment authorization can prevent the hiring of unauthorized workers, which can lead to serious consequences, including hefty fines and damage to the company’s reputation. Failing to verify employment authorization can lead to legal penalties, fines, and the potential loss of business licenses.
The process of completing the Form I-9 involves several steps. First, the employee must complete Section 1 of the form, providing personal information and attesting to their employment authorization. Next, the employer must complete Section 2, reviewing the employee’s documents and certifying their authenticity. Finally, the employer must retain the form for a specified period and make it available for inspection by authorized government officials.
An option for employers to ensure proper documentation of workers is to utilize the Federal government’s E-Verify system. This is an online system used by employers to confirm the eligibility of their employees to work in the U.S. Employers enter information from an employee’s Form I-9 into the system, which then checks this data against government records. This helps ensure that the employee is legally authorized to work. E-Verify is used by businesses of all sizes to maintain compliance with employment laws.
Source: This Tutorial has been adapted from "Human Resources Management" by Lumen Learning. Access for free at courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-humanresourcesmgmt/. License: CC BY: Attribution.