Table of Contents |
The DuPont equation is a means of calculating return on equity (ROE) based on three components:
In the DuPont equation, ROE equals profit margin multiplied by asset turnover multiplied by financial leverage, where each component can be broken down into further calculations.
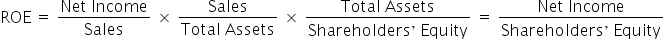
ROE measures the rate of return on the ownership interest or shareholders’ equity of the common stock owners. It is a measure of a company’s efficiency in generating profits using the shareholders’ stake of equity in the business. In other words, ROE is an indication of how well a company uses investment funds to generate earnings growth. It is also commonly used as a target for executive compensation, since ratios such as ROE tend to give management an incentive to perform better.
By splitting ROE into three parts, companies can more easily understand changes in their ROE over time. Let’s take a closer look at the three components of the DuPont equation:
IN CONTEXT
As you are learning, ROE is a measure of how a company uses its shareholders’ equity in the business to earn a profit. Assume that Alphabet Inc., parent company to Google, has a current ROE of 26.04%. Even though that is an impressive ROE, Alphabet strives for continual improvement and wants to examine this return.
Using the ROE formula, Alphabet can only see a part of the story.
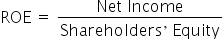
The problem with this equation is that ROE is multifaceted, and using this equation does not give the company or the investors the full picture. This is where the DuPont equation steps in. The DuPont equation dives deeper into the components of ROE, so the individual pieces can be studied, and potential action can be taken to improve one or many of the components. You can find the component pieces in Alphabet’s financial statements:
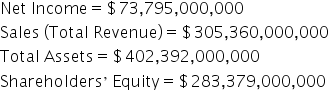
Now, let’s apply the DuPont formula to our example:
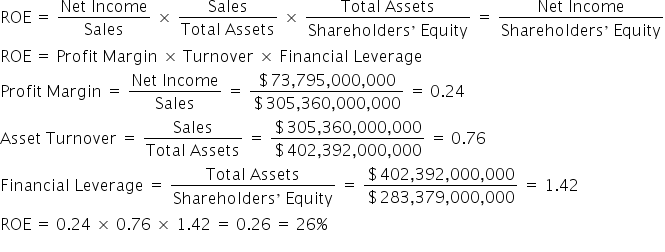
Using the component pieces of ROE, Alphabet can determine which, if any, of these parts can be worked on to increase the ROE.
A high ROE does not necessarily mean that a company will see immediate benefits. Stock prices are most strongly determined by earnings per share (EPS) as opposed to ROE. EPS is the amount of earnings for each outstanding share of a company’s stock. EPS is equal to profit divided by the weighted average of common shares.
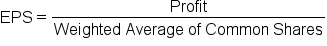
The true benefit of a high ROE comes from a company’s earnings being reinvested into the business or distributed as a dividend. In fact, ROE is presumably irrelevant if earnings are not reinvested or distributed.
Source: THIS TUTORIAL HAS BEEN ADAPTED FROM "BOUNDLESS FINANCE" PROVIDED BY LUMEN LEARNING BOUNDLESS COURSES. ACCESS FOR FREE AT LUMEN LEARNING BOUNDLESS COURSES. LICENSED UNDER CREATIVE COMMONS ATTRIBUTION-SHAREALIKE 4.0 INTERNATIONAL.