Table of Contents |
We now look at identities which we can use to evaluate trigonometric expressions when the angle is a sum or difference of two other angles.
If A and B are angles, then we have the following identities.

One way to use these identities is to find exact values of cosines of sums and differences of special angles.
EXAMPLE
Note that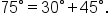 Use this fact to find
Use this fact to find 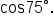
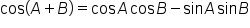
|
This is the identity used. |
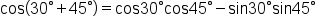
|
Replace A with 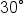 and B with and B with 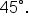
|
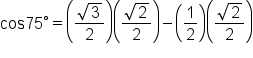
|
Replace all trigonometric functions with their exact values. |
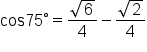
|
Simplify. |
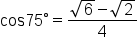
|
Write the result as a single fraction. |
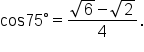 Note that this exact value is quite more complicated than the exact values we’ve learned for our special angles. While it’s useful to be able to find an exact value for
Note that this exact value is quite more complicated than the exact values we’ve learned for our special angles. While it’s useful to be able to find an exact value for 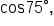 it is not very useful to memorize it.
it is not very useful to memorize it.
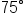 is equal to
is equal to 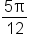 radian. This means that
radian. This means that 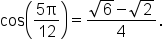
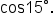
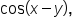 where values of
where values of 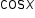 and
and 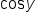 are known.
are known.
EXAMPLE
Given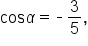 where
where 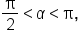 and
and 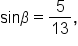 where
where 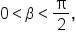 find the exact value of
find the exact value of 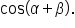
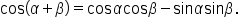
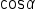 and
and 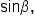 but not
but not 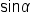 and
and 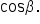 These can be found using Pythagorean identities.
These can be found using Pythagorean identities.
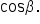 Since
Since 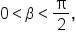 we know
we know 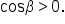
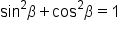
|
This is the identity to use when given 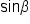 and we want to find and we want to find 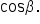
|
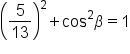
|
Replace 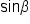 with with 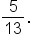
|
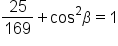
|
Simplify. |
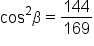
|
Subtract 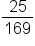 from both sides. from both sides.
|
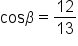
|
Apply the square root principle. Since 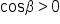 for a quadrant I angle, only the positive solution is considered. for a quadrant I angle, only the positive solution is considered.
|
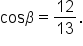
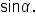 Since
Since 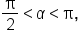 we know
we know 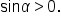
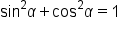
|
This is the identity to use when given 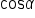 and we want to find and we want to find 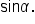
|
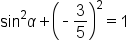
|
Replace 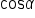 with with 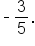
|
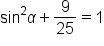
|
Simplify. |
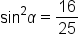
|
Subtract 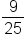 from both sides. from both sides.
|
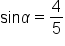
|
Apply the square root principle. Since 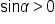 for a quadrant I angle, only the positive solution is considered. for a quadrant I angle, only the positive solution is considered.
|
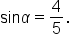
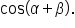
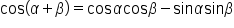
|
This is the sum of angles identity. |
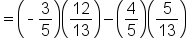
|
Replace all trigonometric functions of  and and 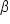 with their values. with their values.
|
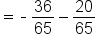 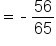
|
Simplify. |
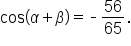
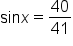 and
and 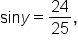 where both x and y are acute angles.
where both x and y are acute angles.
Sum and difference formulas can also be used to simplify expressions.
EXAMPLE
Use an appropriate identity to simplify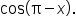
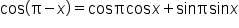
|
Use the cosine of a difference of angles identity. |
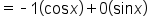
|
Replace 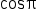 and and 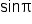 with their values. with their values.
|
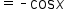
|
Simplify. |
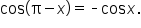
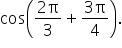
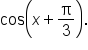
Similar to the cosine formulas, we have the following:

Let’s use these identities to find exact values.
EXAMPLE
Find the exact value of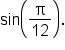
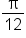 is equal to
is equal to 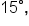 which is
which is 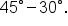 Thus, using radians, we write
Thus, using radians, we write 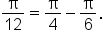
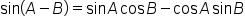
|
This is the identity we will use. |
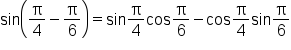
|
Replace A with 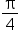 and B with and B with 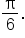
|
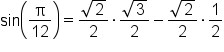
|
Find the exact value of each trigonometric function. |
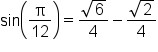
|
Simplify. |
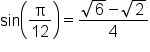
|
Write as a single fraction. |
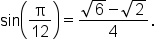
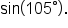
Now, let’s simplify expressions.
EXAMPLE
Use an appropriate identity to expand the expression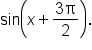
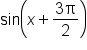
|
This is the expression we are going to expand. |
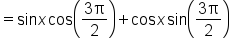
|
Apply the sine of a sum of angles identity. |
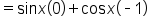
|
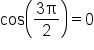 and and 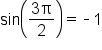
|
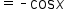
|
Simplify. |
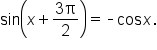
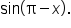
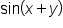 when given values of other trigonometric functions of x and y.
when given values of other trigonometric functions of x and y.
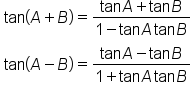
EXAMPLE
Find the exact value of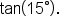
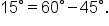
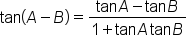
|
This is the identity that is used. |
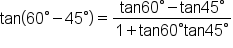
|
Replace A with 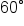 and B with and B with 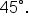
|
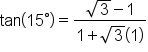
|
Replace 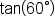 and and 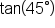 with their exact values. with their exact values.
|
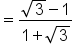
|
Simplify. |
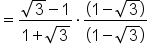
|
Rationalize the denominator. |
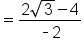
|
Perform the multiplications. |
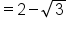
|
Perform the division; write the positive term first. |
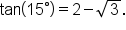
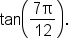
EXAMPLE
Given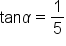 and
and 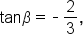 find the exact value of
find the exact value of 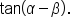
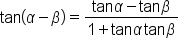
|
This is the difference of angles identity for tangent. |
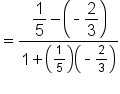
|
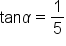 and and 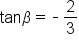
|
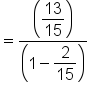
|
Simplify the numerator and denominator. |
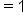
|
Simplify. |
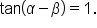
Notice that we didn’t need quadrant information for the angles in this problem. That is because we were given values of the tangent function, and that is all that was required to use in the difference of angles identity.
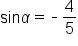 and
and 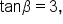 where
where 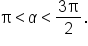
EXAMPLE
Use an appropriate identity to write an expanded expression for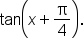
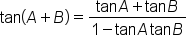
|
This is the identity that is used. |
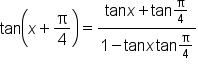
|
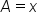 and and 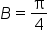
|
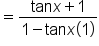
|
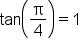
|
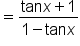
|
Simplify. |
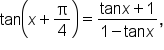 which could also be written as
which could also be written as 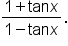
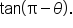
We apply the same concepts that we did earlier. The only new challenge is that sum and difference identities may be used.
EXAMPLE
Verify that the equation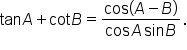
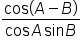
|
Start with the right side since it can be manipulated; the left side is simplified. |
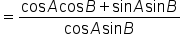
|
Use the cosine of a difference of angles identity in the numerator. |
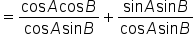
|
Split the expression into single fractions. |
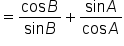
|
Cancel common factors in each fraction. |
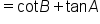
|
Use the quotient identities. |
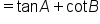
|
Addition is commutative; rewrite in order to match the left side of the original equation. |
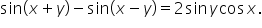
SOURCE: THIS WORK IS ADAPTED FROM PRECALCULUS BY JAY ABRAMSON. ACCESS FOR FREE AT OPENSTAX.ORG/BOOKS/PRECALCULUS/PAGES/1-INTRODUCTION-TO-FUNCTIONS