Table of Contents |
You may wonder why we are discussing economic systems in a business class! Understanding economics is a key ingredient of business success for several reasons.
EXAMPLE
If we run a coffee shop and are importing coffee beans from another part of the world, it is important to understand economic systems. This can also help us in understanding location, expansion, and pricing decisions.When a business understands the factors of production, it is better able to allocate resources to meet its goals, manage business costs, plan for growth and innovation, and also be informed about strategic planning. The factors of production are merely the resources necessary to produce output for a business. Factors of production include the following:
| Factor of Production | Example | Details/Definition | Characteristics | How Revenue Is Earned |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Resources | Farmland and fishing sites | Land, bodies of water, and minerals | Limited in nature | Rent earning |
| Labor and Knowledge | White- and blue-collar job skills | Physical and mental efforts | Skill development | Wage earning |
| Capital | Software and factories | Instruments for production, production sites (building or outdoors) | Require productivity and investment strategies | Interest earning |
| Entrepreneurship | Start-up founders and business executives | Innovation and risk-taking | Profit driven; organizes all other factors of production | Profit earning |
Materials that are useful inputs in their natural state are known as natural resources. They include farmland, forests, mineral and oil deposits, and water. Sometimes, natural resources are simply called land, although, as you can see, the term means more than just land. Companies use natural resources in different ways.
EXAMPLE
 The International Paper Company uses wood pulp to make paper, and the Pacific Gas & Electric Company may use water, oil, or coal to produce electricity.
The International Paper Company uses wood pulp to make paper, and the Pacific Gas & Electric Company may use water, oil, or coal to produce electricity.
Today, urban sprawl, pollution, and limited resources have raised questions about resource use. Conservationists, environmentalists, and government bodies are proposing laws to require land-use planning and resource conservation.
Labor, or human resources, refers to the economic contributions of people working with their minds and muscles. This input includes the talents of all people—from a restaurant cook to a nuclear physicist—who perform the many tasks of manufacturing and selling goods and services.
Knowledge refers to the combined talents and skills of the workforce and has become a primary driver of economic growth. Today’s competitive environment places a premium on knowledge and learning over physical resources. Despite the fact that many “routine” jobs have been replaced by automation over the last decade or outsourced to other countries, technology has actually created more jobs that require knowledge and cognitive skills.
The tools, machinery, equipment, and buildings used to produce goods and services and get them to the consumer are known as capital.
Entrepreneurs are the people who combine the inputs of natural resources, labor, and capital to produce goods or services with the intention of making a profit or accomplishing a not-for-profit goal. These people make the decisions that set the course for their businesses; they create products and production processes or develop services. Because they are not guaranteed a profit in return for their time and effort, they must be risk-takers. Of course, if their companies succeed, the rewards may be great.
Let’s consider a small coffee shop and how the factors of production might be used:
IN CONTEXT: A Coffee Shop's Factors of Production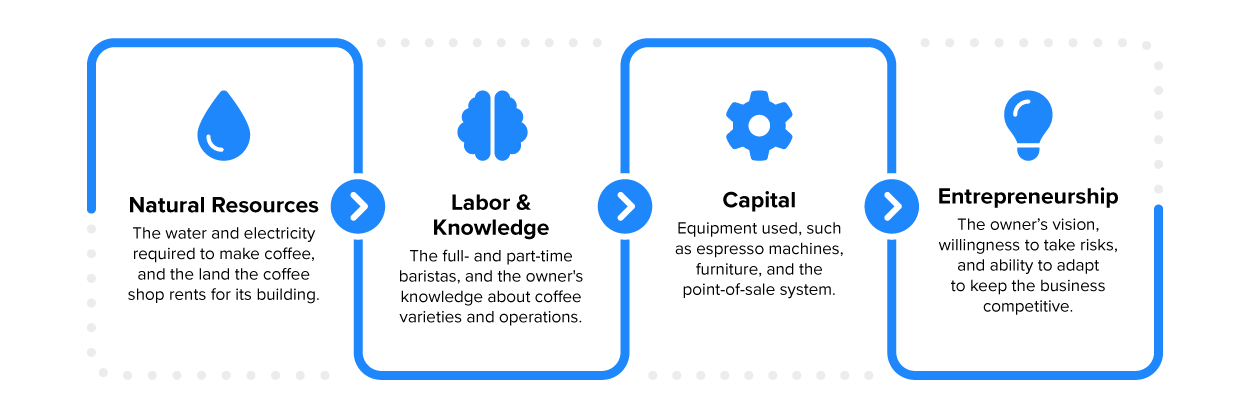
Economic systems are how a society chooses to produce, distribute, and consume its goods, services, and resources. The following are the two broad categories of economic systems, but we will also discuss a traditional economy and a mixed market economy:
A planned economy is one in which a central authority controls and chooses how to distribute resources for the production of goods and services.
There are two major types of planned economies:
EXAMPLE
In the modern world, we see communism active in places like North Korea and Cuba.Under socialism, the government owns select businesses or pieces of the economy. This system is found predominantly throughout Europe.
EXAMPLE
 Under the National Health System in the United Kingdom, the government decides how health care is distributed among the populace.
Under the National Health System in the United Kingdom, the government decides how health care is distributed among the populace.
The following are some of the key features of a planned economy:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
The next type of economy we’re going to look at is the market economy. This is where supply and demand dictate how to distribute resources for the production of goods and services. You might have heard of this type of economy being referred to as capitalism.
In this market economy, private owners are responsible for and focused on the development of wealth. These private owners and their consumers get to drive how the market works. They control what’s produced based on the supply from the producers and the demand from the consumers.
Key features include the following:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
The United States is a mixed market economy, which is a combination of a planned economy and a market economy, but the United States operates differently from other countries around the world. It’s more laissez-faire than China or France.
The term “laissez-faire” comes from French, meaning “leave alone or let do.” It was primarily used by 18th-century French economists like Francois Quesnay. The concept originated within the system of free-market capitalism, advocating minimal to no government intervention, regulations, or restrictions. Its main goal is to facilitate buying and selling in the market, thereby fostering an environment that encourages growth and development.
Now, an interesting thing about markets around the world currently is the privatization of state-owned businesses in places such as Sweden, France, or India, like the Air India and Air France examples from earlier. What you see now is an increased tendency to divest those businesses from the government and put them into private hands.
EXAMPLE
Lufthansa Airlines from Germany was completely state owned up until 1994, at which point the government divested itself of the airline. It is now run as a private company.The following are the key features of a mixed market economy:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|

A traditional economy is the earliest form of economic system. It is characterized by customs, traditions, and historical practices when making decisions about how resources are utilized for the production and distribution of goods and services. It is marked by bartering instead of the use of currency, with people relying on subsistence farming, hunting, and crafting. Skills and knowledge are passed down through generations.
Key features include the following:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Let’s compare examples of the different types of economic systems that we’ve seen in this lesson:
| Economic System | Example | Ownership | Decision-Making | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planned | Cuba / North Korea | Government | Central planning | Promotes reduced inequality and fast decision-making | Inefficiency and inequality |
| Market | Japan | Private | Demand and supply | High efficiency and high innovation | Market failure and inequality |
| Mixed Market | Sweden / Germany | Government and private | Market and government | Balanced economic growth, development, and welfare | Long decision-making period (debates) and bureaucracy |
| Traditional | Amish / Maasai | Communal and families | Customs and traditions | Strong community and promotes sustainability | Low innovation and stagnation |
Source: THIS CONTENT HAS BEEN ADAPTED FROM RICE UNIVERSITY’S “INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS”. ACCESS FOR FREE AT OpenStax. LICENSE: CREATIVE COMMONS ATTRIBUTION 4.0 INTERNATIONAL.
REFERENCES
Beaton, C. (2017, January 26). Why knowledge workers are bad at making decisions. Forbes.
Zumbrun, J. (2016, May 4). The rise of knowledge workers is accelerating despite the threat of automation. Wall Street Journal.