In this lesson, you will learn about the structure and function of the Golgi body in cells. Specifically, this lesson will cover:
-
Augmented Reality in Human Biology
At the end of this tutorial, you will have an opportunity to use AR to review and supplement some of the figures from Challenge 1.2. Remember, AR resources are
not required, but may enhance your learning experience. To use AR, you will need a phone or tablet with a camera and browser. Scan this QR code for a reminder on tips and tricks for using Sophia AR.

If you’re on a laptop or desktop computer:
Scan the QR code using the camera on your smartphone or tablet.
If you are on a phone or tablet
click here.
1. Golgi Body Overview
The Golgi body is a cell organelle that is found in eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a nucleus, such as your own cells. The Golgi body is an organelle only found in eukaryotic cells.
-
The Golgi body is sometimes referred to as the Golgi apparatus. You might hear it either way, but it's the same organelle and has the same function.
-
-
- Golgi Body
- A cell organelle that packages lipids and proteins to be transported out of the cell.
2. Golgi Body Function
The function of the Golgi body is to modify, package, and transport materials throughout the cell. The Golgi body, like the endoplasmic reticulum, is a part of the endomembrane system.
The endomembrane system is a system that makes lipids, modifies proteins, and packages molecules to send them out to various parts of the cell.
-
-
- Endomembrane System
- A system of cellular structures, including the endoplasmic reticulum, nuclear envelope, Golgi body, and vesicles, that is used to synthesize and package proteins and lipids.
- Lipid
- A hydrophobic (water-repelling) biomolecule made up of glycerol and fatty acids; lipids include phospholipids, cholesterol and steroid hormones.
3. Golgi Body Structure
The Golgi body looks like a bunch of flattened sacs (or "pancake stacks") between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the plasma membrane.
Within the Golgi body, there are enzymes. The enzymes help to finish the production of proteins and lipids that began in the endoplasmic reticulum.
-
The endoplasmic reticulum is like the assembly line that helps to assemble the proteins and lipids. From there, they're sent to the Golgi body, where they're finished off and then packaged. Once they're finished off, they're packaged into something called a
vesicle.
The image below shows a Golgi body with the vesicles labeled.
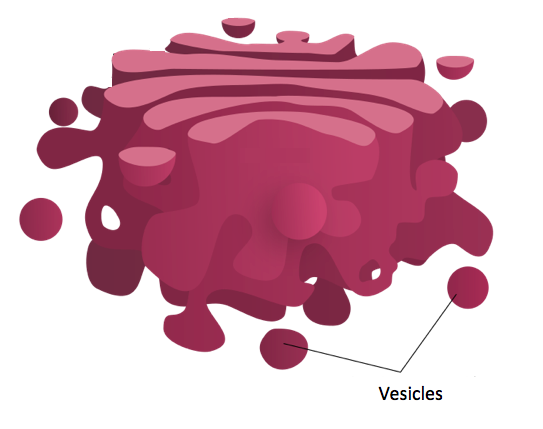
These vesicles are tiny sacs that contain the finished product and will transport the finished product from the Golgi apparatus, through the cytoplasm, to wherever it needs to go in the cell.
The vesicle will have a specific location that it needs to go to in the cell. That location will be determined by enzymes, or different tag molecules, that are added to that vesicle. These tag molecules tell the vesicle where it needs to go within the cell.
Some vesicles are used to transport different molecules throughout the cell, but other types of vesicles can contain enzymes that will help to break down substances within the cell.
One type of vesicle within a cell that you might be familiar with is a lysosome. Enzymes contained in the lysosome will help break down materials in the cell, such as cell parts or bacteria. Anything that the cell does not want to have within it can be broken down by lysosomes.
-
Vesicles are used to either transport substances or to break down substances within the cell.
-
-
- Vesicle
- A small sac surrounded by a membrane which transports cellular products within the endomembrane system.
-

Explore eukaryotic cells in three dimensions using augmented reality (AR)!
If you’re on a laptop or desktop computer:
Scan the QR code using the camera on your smartphone or tablet.
If you are on a phone or tablet
click here.
-
If you're taking the Human Biology Lab course simultaneously with this lecture, it's a good time to try the Building Animal Cells Activity in Unit 2 of the Lab course. Good luck!
This lesson has been an overview of the function and structure of a Golgi body in eukaryotic cells.
Keep up the learning and have a great day!


 Explore eukaryotic cells in three dimensions using augmented reality (AR)!
Explore eukaryotic cells in three dimensions using augmented reality (AR)!